The effects of toe grip training on physical performance and cognitive function of nursing home residents, Journal of Physiological Anthropology
By A Mystery Man Writer
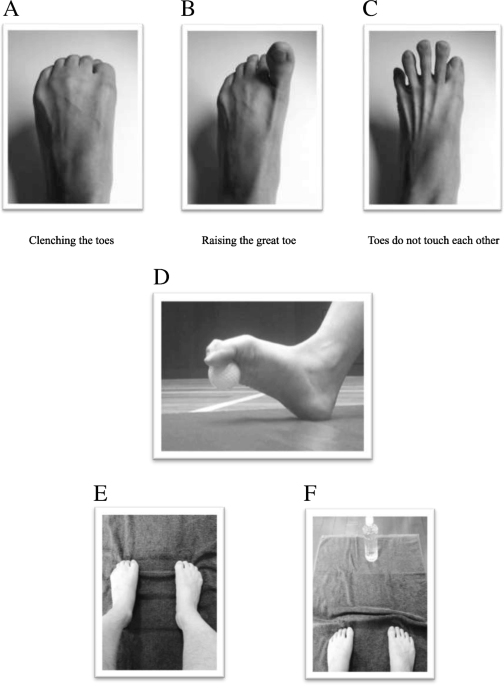
Background Toe grip-related training requires individuals to actively exercise muscles that are not frequently used; therefore, it may improve not only toe grip strength but also cognitive function. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of toe grip-related training on predictors of physical performance and cognitive function in nursing home residents. Methods A total of 35 nursing home residents (35 left and 35 right feet; mean age, 82.1 ± 7.9 years) were included in this study. The participants were divided into two groups: a training group and a control group. The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) was used to assess the cognitive function of the participants, and the Fall Risk Index (FRI) was used to evaluate the risk of falls. Toe grip-related physical function was also assessed. Baseline endpoints were evaluated and the effects of toe grip-related training were examined following a 12-week training intervention. Results The training group showed significant improvements in MMSE score, FRI score, toe grip strength, and the toe skill (TS) test; however, the control group did not show these changes. The training group showed significant increases in Δ MMSE, Δ toe grip strength, and Δ TS (right foot) than the control group. Stepwise regression analysis revealed that Δ toe grip strength is an independent factor of Δ MMSE. Conclusions Toe grip training improves not only toe grip strength itself, but also cognitive function. Furthermore, change in toe grip strength was an independent factor of change in MMSE in those populations. Trial registration UMIN, UMIN000027437 . Registered on 26 May 2017.

Case Study Age Related Macular Degeneration

Association of mobility capacity with the masses and amounts of intramuscular non-contractile tissue of the trunk and lower extremity muscles in community-dwelling older adults - ScienceDirect
Full article: Accepted Abstracts from the International Brain Injury Association's 12th World Congress on Brain Injury

Effects of high-load and low-load resistance training in patients with coronary artery disease: rationale and design of a randomised controlled clinical trial

Publikationer

Oxford textbook of neurorehabilitation. 9780199673711, 0199673713

Urinary Incontinence Is Associated With Physical Performance Decline in Community-Dwelling Older Women: Results From the International Mobility in Aging Study - Luana Caroline de Assunção Cortez Corrêa, Catherine M. Pirkle, Yan Yan
Peripheral neuropathies, Manual of Neurological Signs
Neurotechnologies to restore hand functions

PDF) The effects of toe grip training on physical performance and cognitive function of nursing home residents
- Dr Buzby's Medium ToeGrips for Dogs,Instant Traction on Wood/Hardwood Floors,Dog Anti Slip Relief,Dog Grippers for Senior Dogs,Stop Sliding

- Sure-Grip Gripper Speed Skate Toe Stops/Guards

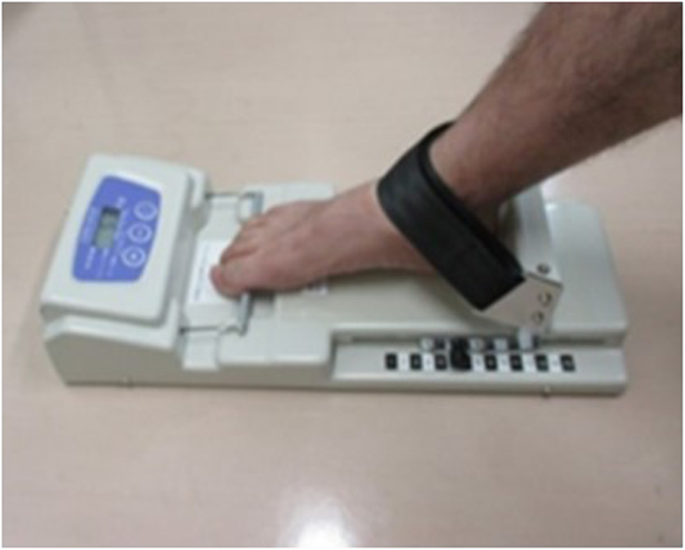
- Toe grip force of the dominant foot is associated with fall risk in community-dwelling older adults: a cross-sectional study, Journal of Foot and Ankle Research
- Why Wear Five-Toe Grip Socks? - Pilates Expert Courtney Miller on Vimeo
- Dr Buzby's Anti Slip Toe Grips for Dogs — My Animal Dispensary




)
