Genetic Determinants of Height Growth Assessed Longitudinally from
By A Mystery Man Writer
Author Summary Family studies have shown that adult height is largely genetically determined. Identification of common genetic factors has been expedited with recent advances in genotyping techniques. However, factors regulating childhood height growth remain unclear. We investigated genetic variants of adult height for associations with peak height velocity in infancy (PHV1) and puberty (PHV2) and timing of pubertal growth spurt in a population based sample of 3,538 Finns born in 1966. Most variants studied associated with adult height in this sample. Of the 48 genetic variants tested, seven of them associated with PHV1 and five with PHV2. However, only one of these associated with both, and we found suggestive evidence for differential effects at different stages of growth for some of the variants. In this sample, less than half of the variants associated with adult height had a measurable effect on PHV1 or PHV2. However, these differences may reflect lower statistical power to detect associations with height velocities compared to adult height. This study provides a foundation for further biological investigation into the genes acting at each stage of height growth.

Trans-ancestral genome-wide association study of longitudinal pubertal height growth and shared heritability with adult health outcomes, Genome Biology
Introduction - Anthropometry Nutritional assessment

SPAG17 Gene - GeneCards, SPG17 Protein

The DOT1L rs12982744 polymorphism is associated with osteoarthritis of the hip with genome-wide statistical significance in males
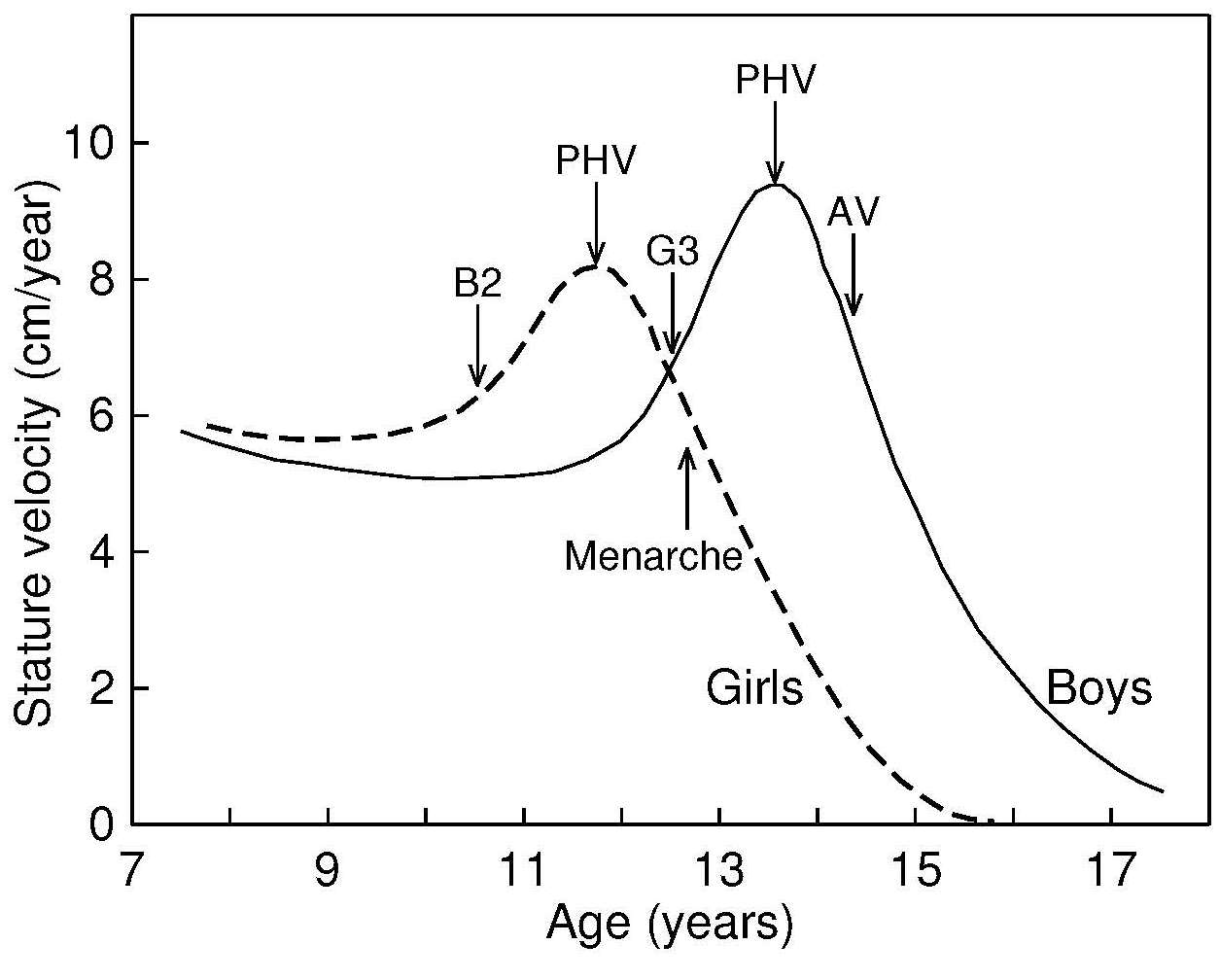
Frontiers Association between height growth patterns in puberty and stature in late adolescence: A longitudinal analysis in chinese children and adolescents from 2006 to 2016
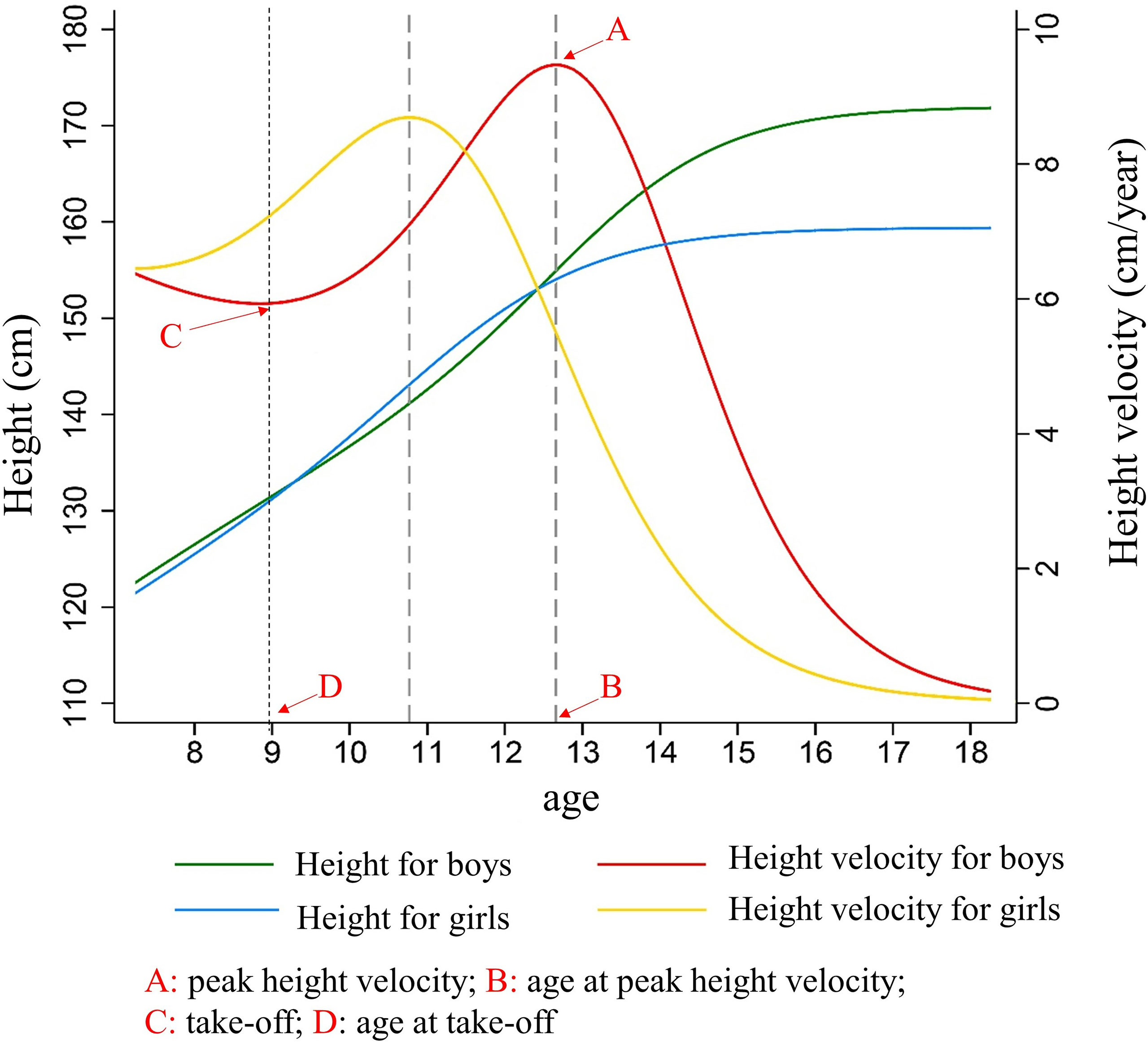
Genetic and environmental influences on height from infancy to early adulthood: An individual-based pooled analysis of 45 twin cohorts

Parameters of pubertal growth spurt in children and adolescents living at high altitude in Peru - ScienceDirect

Growth Hormone Receptor Signaling Pathways and its Negative Regulation by SOCS2
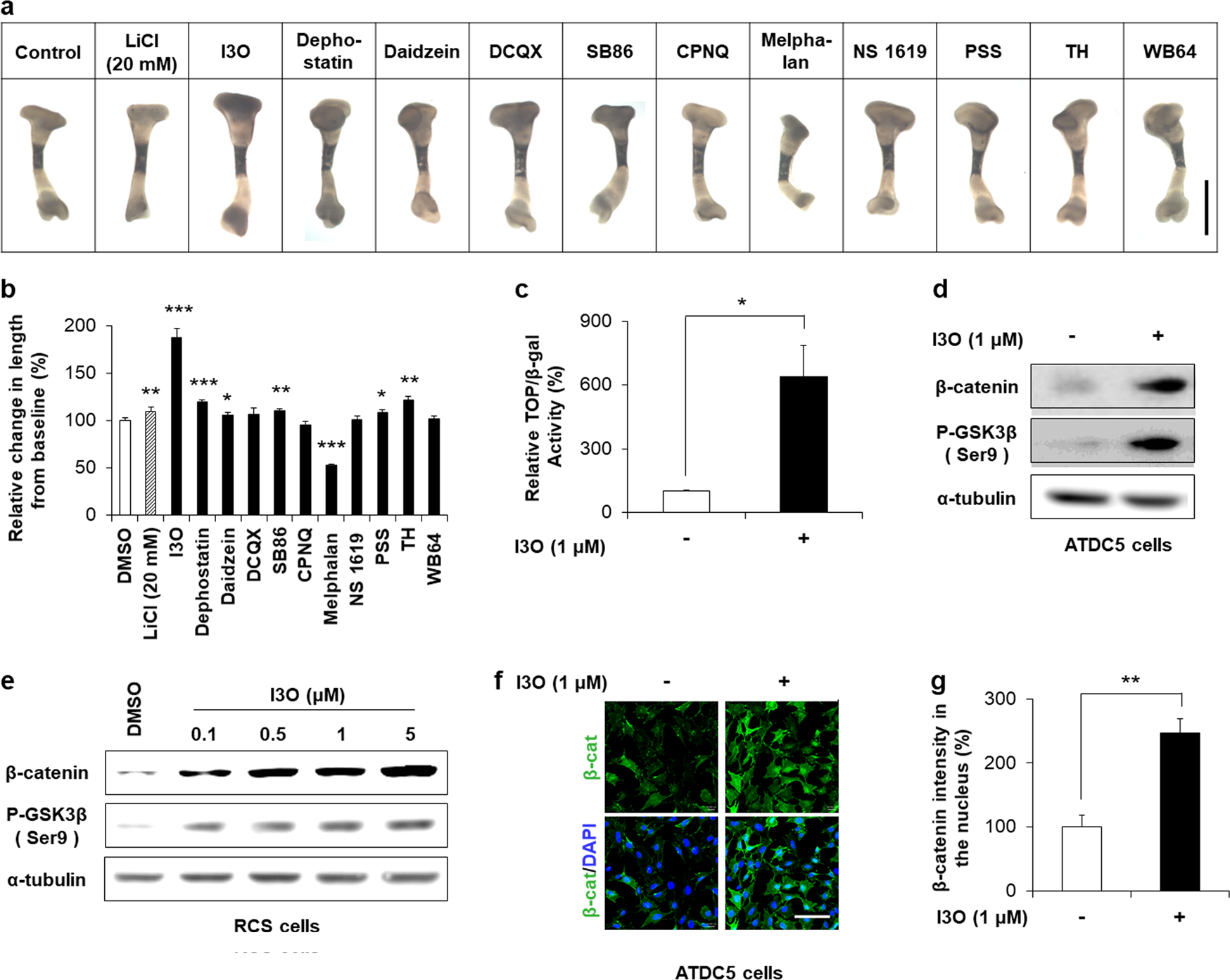
Indirubin-3′-oxime stimulates chondrocyte maturation and longitudinal bone growth via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway

GWAS on longitudinal growth traits reveals different genetic factors influencing infant, child, and adult BMI
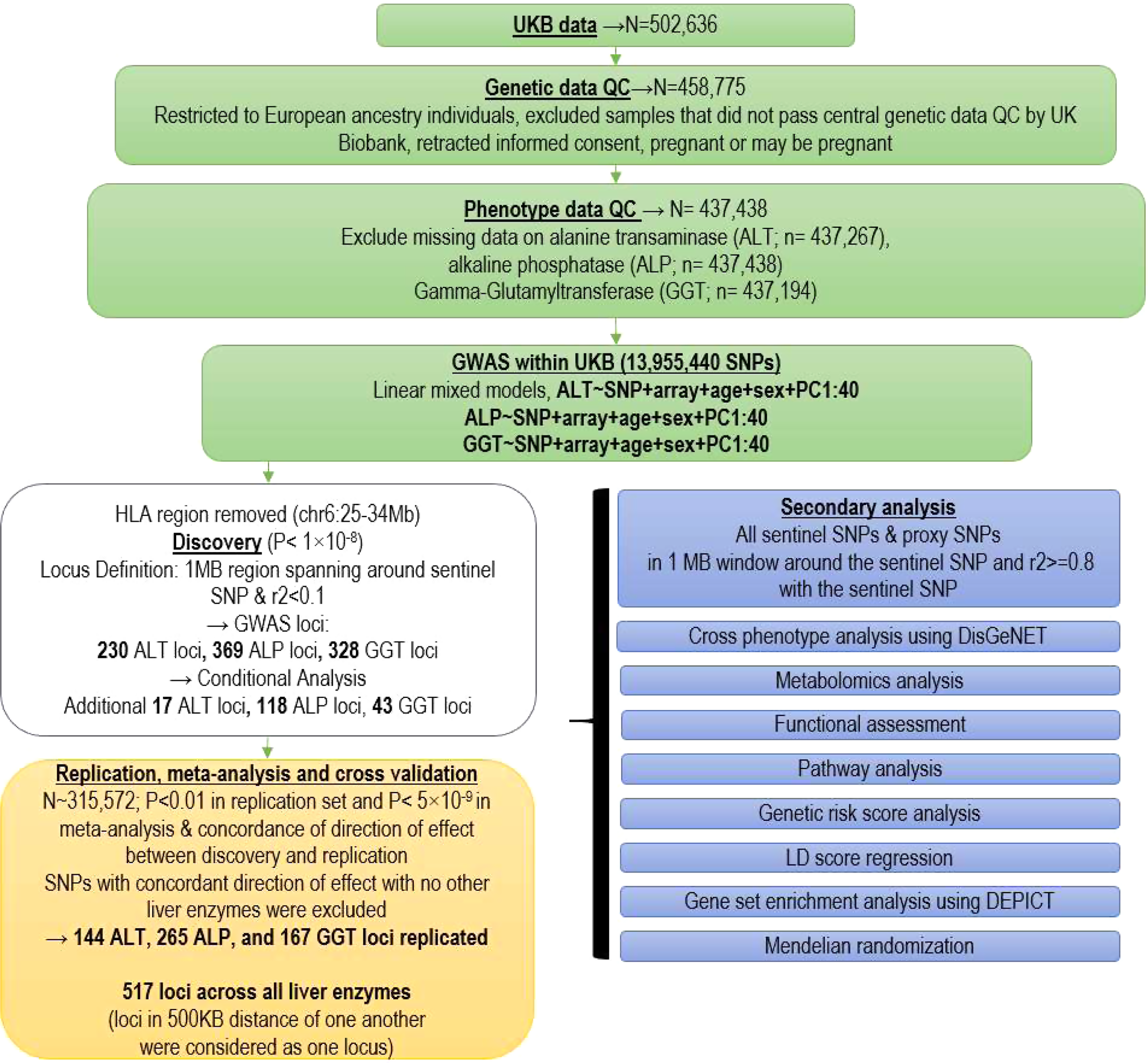
Genetic analysis in European ancestry individuals identifies 517 loci associated with liver enzymes

Associations between SNPs and adult height, peak height velocity in
- Women Boy Shorts Underwear plus Size Bulk Ladies Plus Size Solid

- Ski Clothes, Women's Ski Jacket

- Wrangler Men's George Strait Heavyweight Stone Denim Cowboy Cut Origin - Russell's Western Wear, Inc.

- Soft Wear Slim Jeans with GapFlex

- Maternity Store Near Calgary Canadian Maternity Clothing Stores – Baby & Me Maternity



)

