Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches

By A Mystery Man Writer
Download scientific diagram | Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches in each season. Error bars are one standard error. Data from fall were excluded due to dry conditions at the upper reach. An asterisk next to the season designates a significant difference (α = 0.05) between reaches within that season. from publication: Influence of a Spring on Fish Communities and Habitat in an Ozark Stream | Springs influence water temperature and flow of streams; however, little information exists on the effects of springs on fish communities and their potential as refugia. This study examined the impacts of a spring on a wadeable stream. Fish, water quality, and physical | Fishing Communities, Streams and Upstream | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
Hyperconcentrated floods cause extreme gravel transport through the sandy rivers of the Gangetic Plains
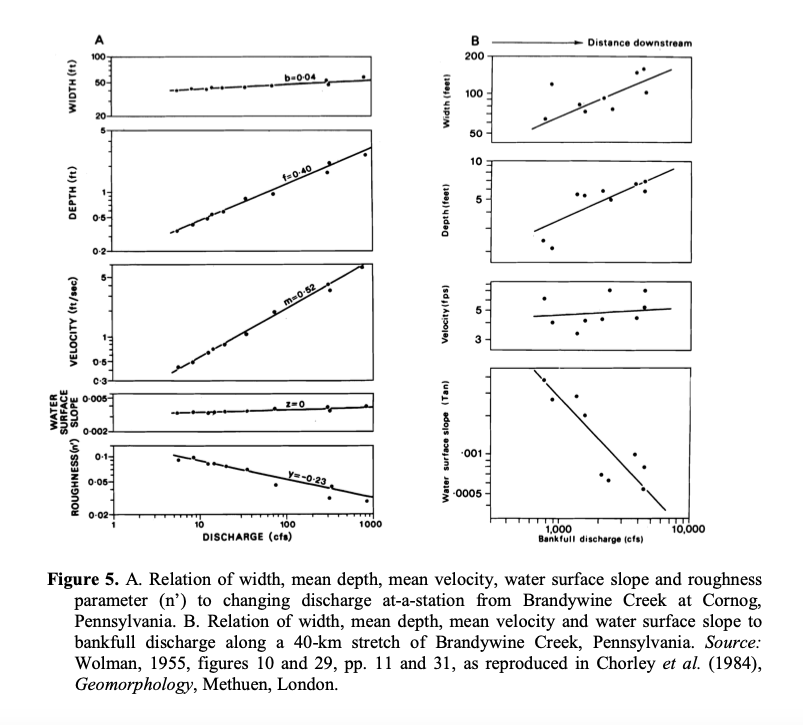
Distance downstream WIDTH (ft) Width (feet) to 40
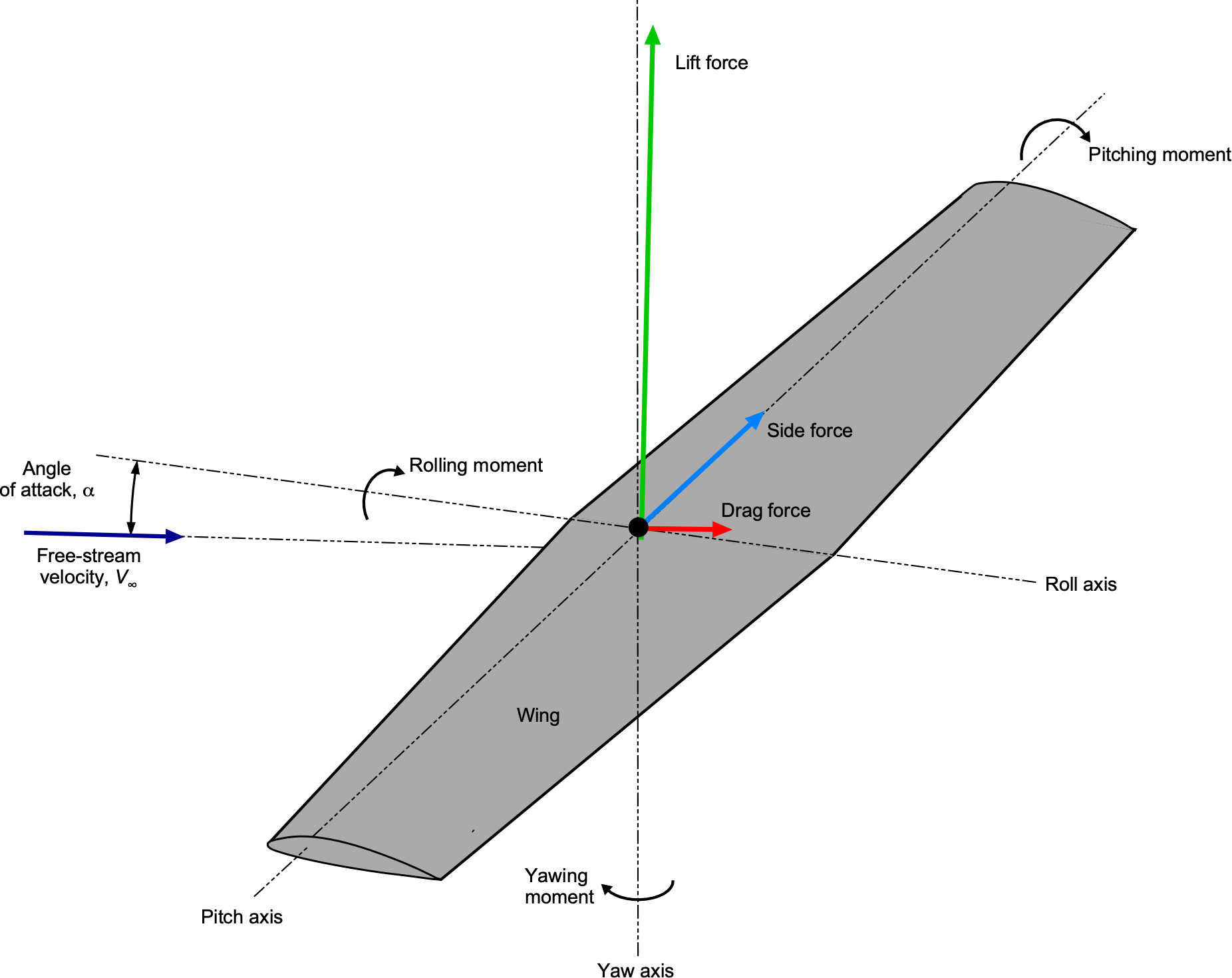
Aerodynamics of Airfoil Sections – Introduction to Aerospace Flight Vehicles
.png)
Newton's Law of Cooling: Definition, Proof, Formulas, & Examples
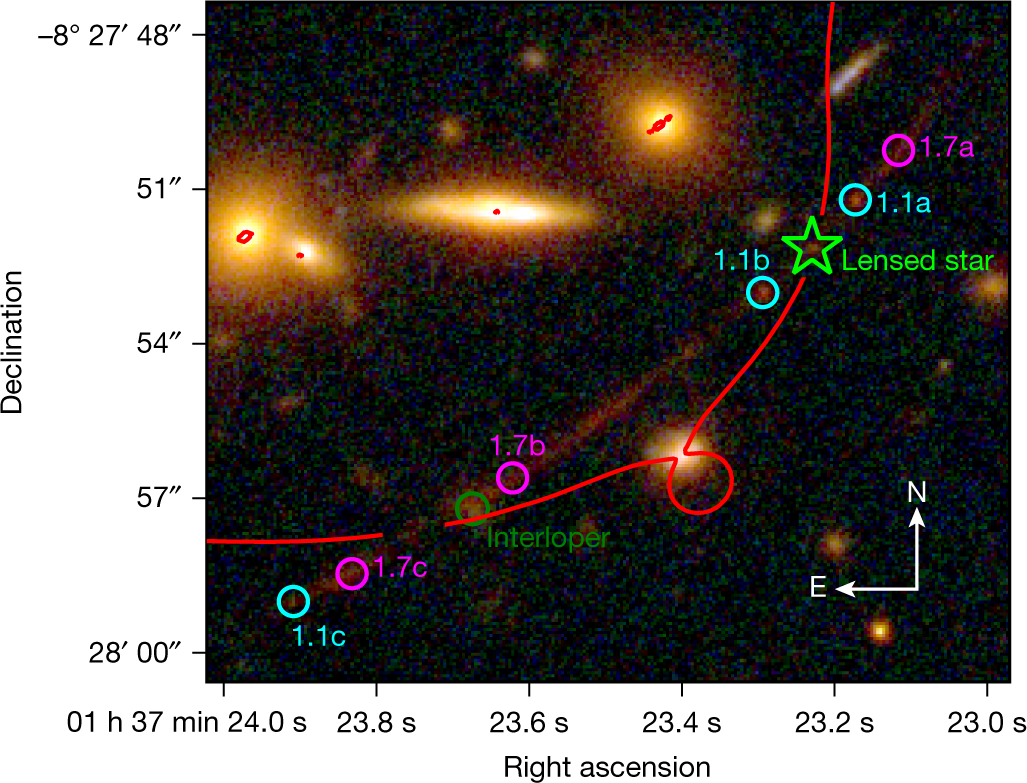
media.springer/full/springer-static/imag

Mean macroinvertebrate biotic index scores ( ± 1SE) for seven sampling

Mid-ocean ridge - Wikipedia
Atmospheric circulation - Wikipedia

PDF) Influence of a Spring on Fish Communities and Habitat in an Ozark Stream
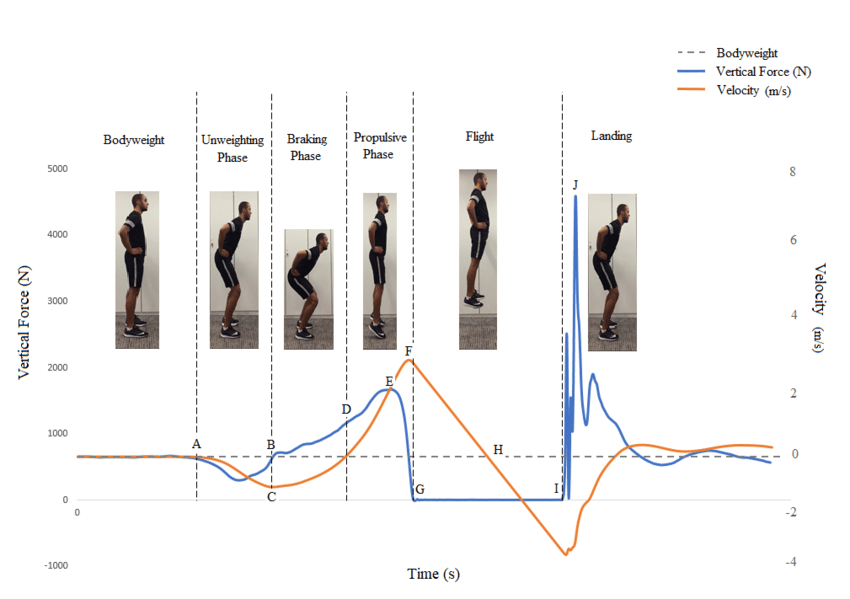
Countermovement Jump (CMJ)

Penetration Depth - an overview
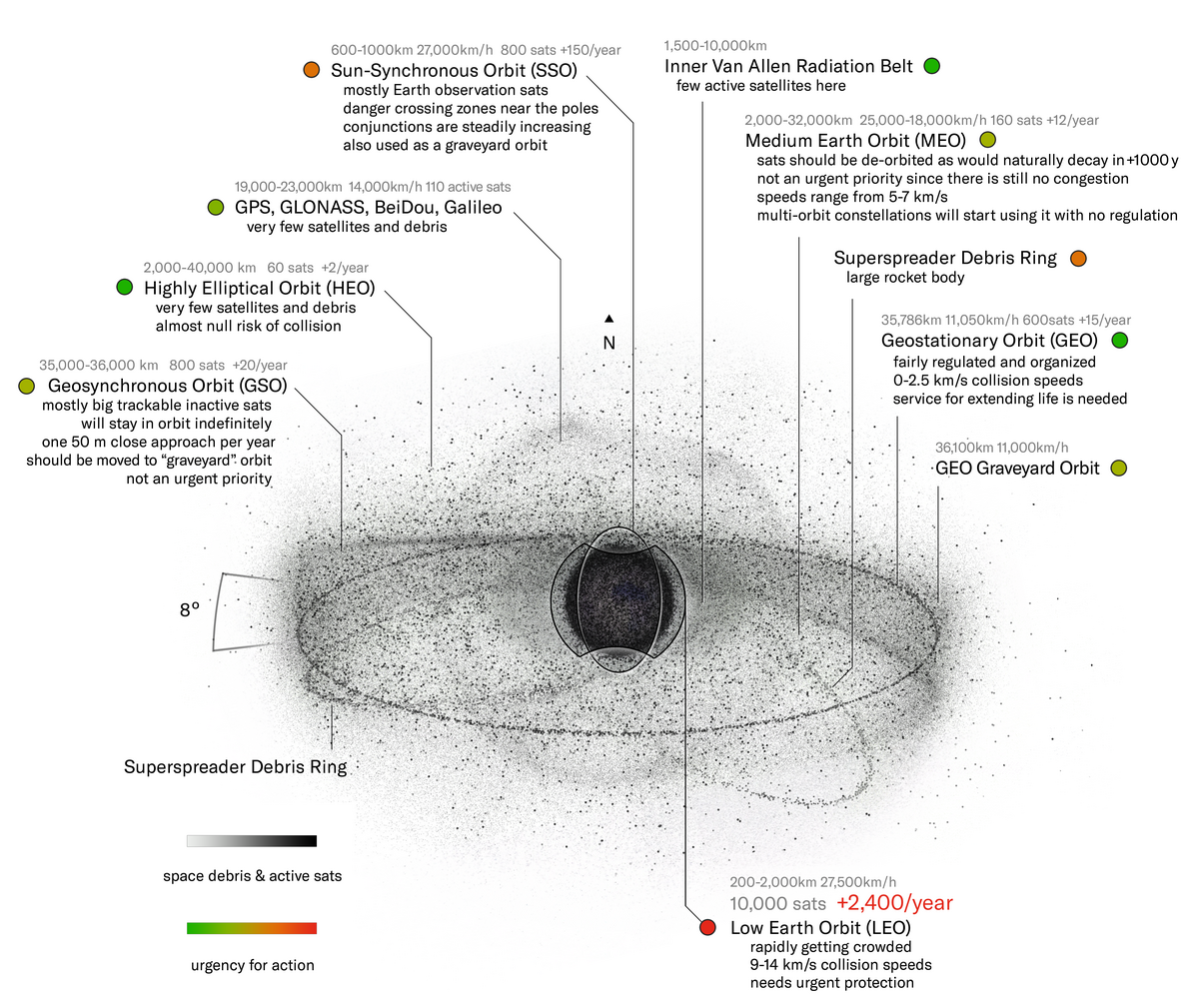
Space debris - Wikipedia
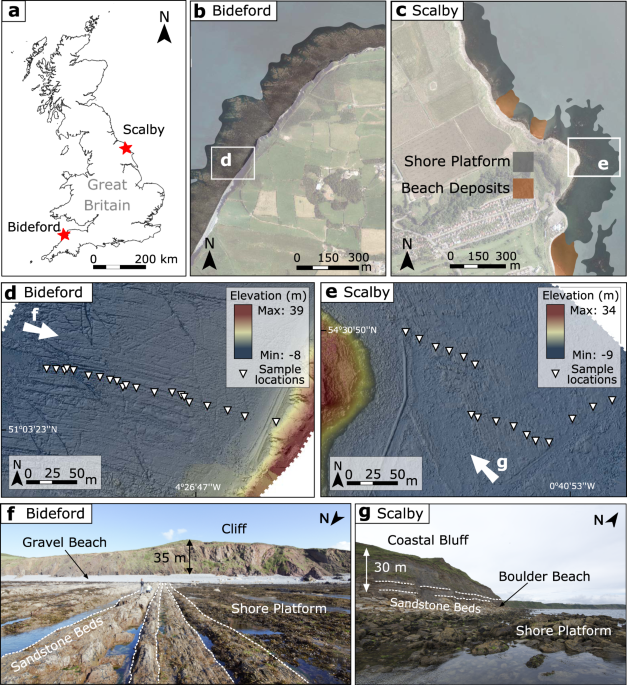
Sea-level rise will likely accelerate rock coast cliff retreat rates

Number of respondents for each scenario
- KATHRINE 69808 - Ronald Joyce Wedding Dress - TDR Bridal Birmingham

- Meridian Legging-GRN - women's leggings - UNDER

- Breast Pad Swimsuit Bra Insert Pads Reusable Silicone Enhancer

- Nintendo Switch 32GB Console - Neon Red / Neon Blue Joy-Con - HADSKABAA HAC-001(-01)

- Selling - [EU] Mystel CHEAP 85€ Valkyrie ilvl 499 full +15 kaia