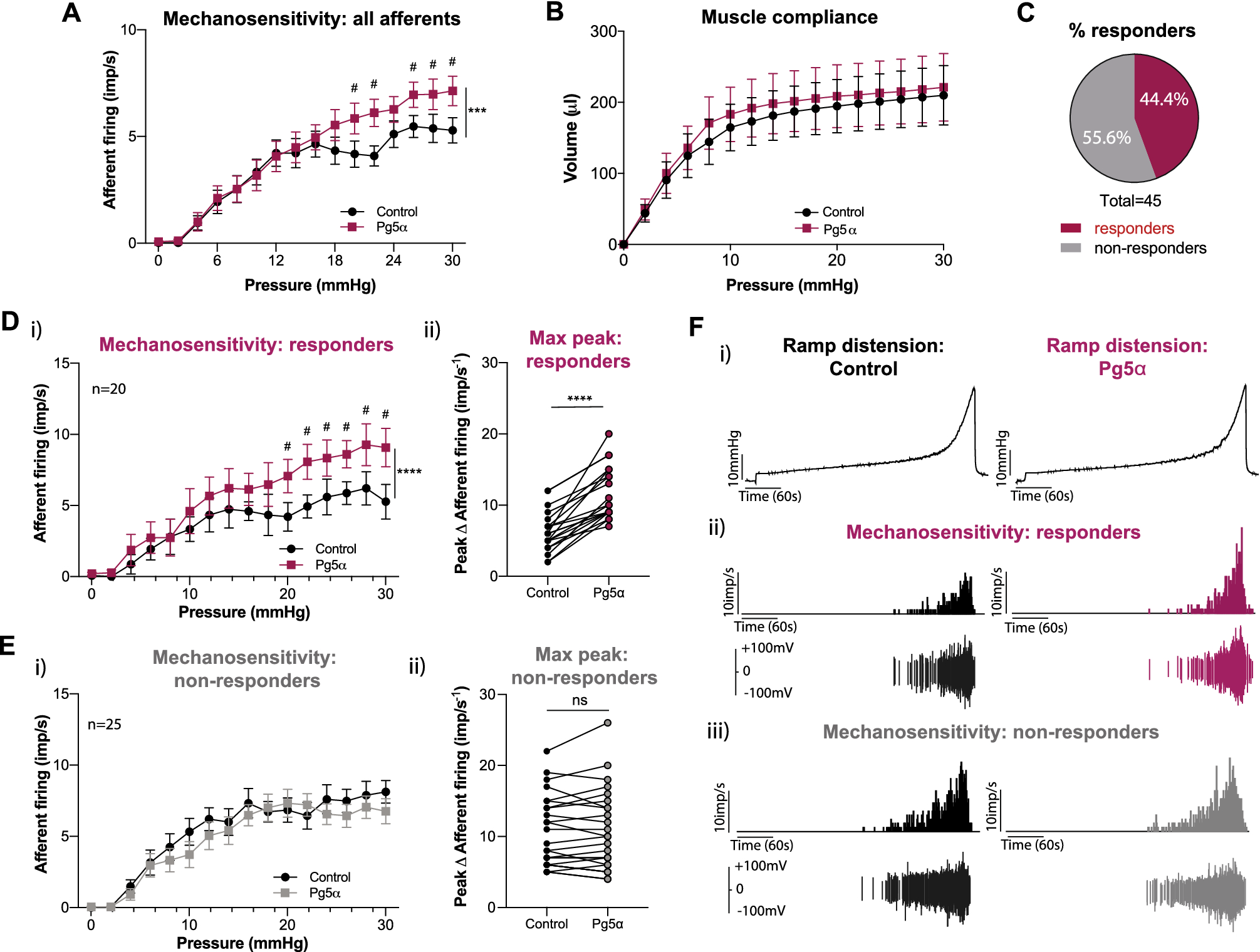
TGR5 agonists induce peripheral and central hypersensitivity to bladder distension
By A Mystery Man Writer
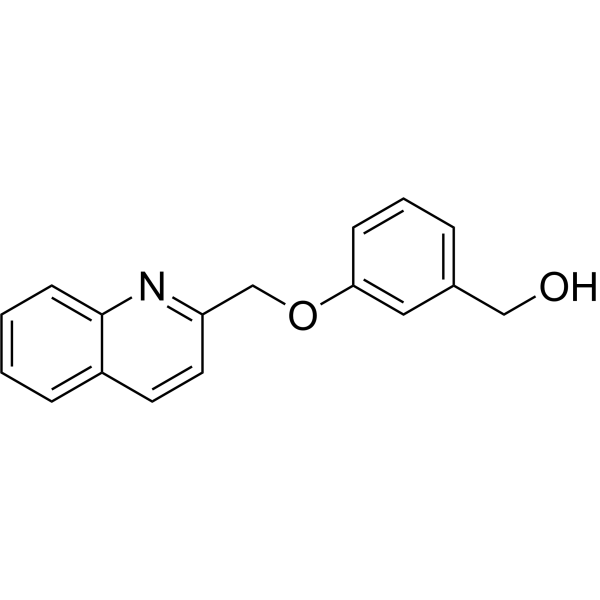
G protein-coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 (Inhibitors Agonists Modulators Antagonists)

Sub-noxious Intravesical Lipopolysaccharide Triggers Bladder Inflammation and Symptom Onset in A Transgenic Autoimmune Cystitis Model: A MAPP Network Animal Study

ERK activation in Lmx1b- but not in Calbindin-expressing neurons in the

ATP activates urothelial cells. (A) Representative trace of a calcium

Bile acids and their receptors in regulation of gut health and diseases - ScienceDirect

TGR5 agonists induce peripheral and central hypersensitivity to bladder distension
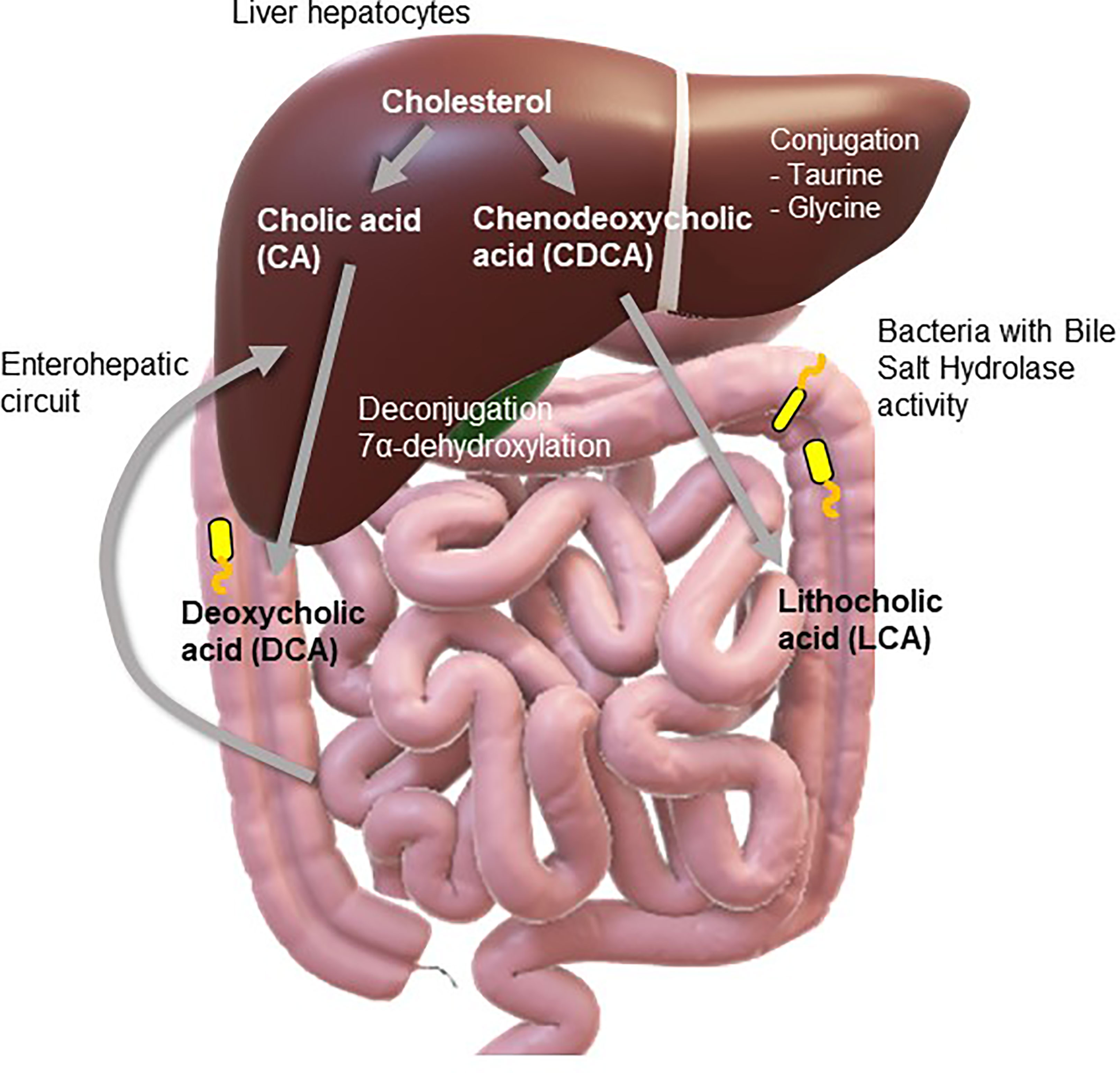
Frontiers Aberrant Gut-To-Brain Signaling in Irritable Bowel Syndrome - The Role of Bile Acids

TRPV4 mediates afferent pathways in the urinary bladder. A spinal c-fos study showing TRPV1 related adaptations in the TRPV4 knockout mouse
Colon-and bladder-innervating dorsal root ganglion neurons are largely

PDF] The TGR5 receptor mediates bile acid-induced itch and analgesia.

Compound 48/80 increases murine bladder wall compliance independent of mast cells

JCI Insight - Chronic linaclotide treatment reduces colitis-induced neuroplasticity and reverses persistent bladder dysfunction

P2Y6-deficiency increases micturition frequency and attenuates sustained contractility of the urinary bladder in mice
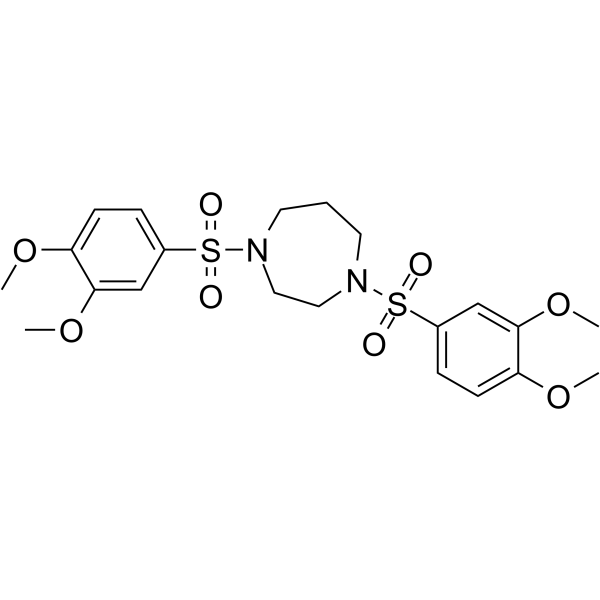
G protein-coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 (Inhibitors Agonists Modulators Antagonists)
G protein-coupled Bile Acid Receptor 1 (Inhibitors Agonists Modulators Antagonists)








