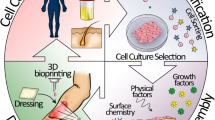
Skin tissue regeneration for burn injury
By A Mystery Man Writer
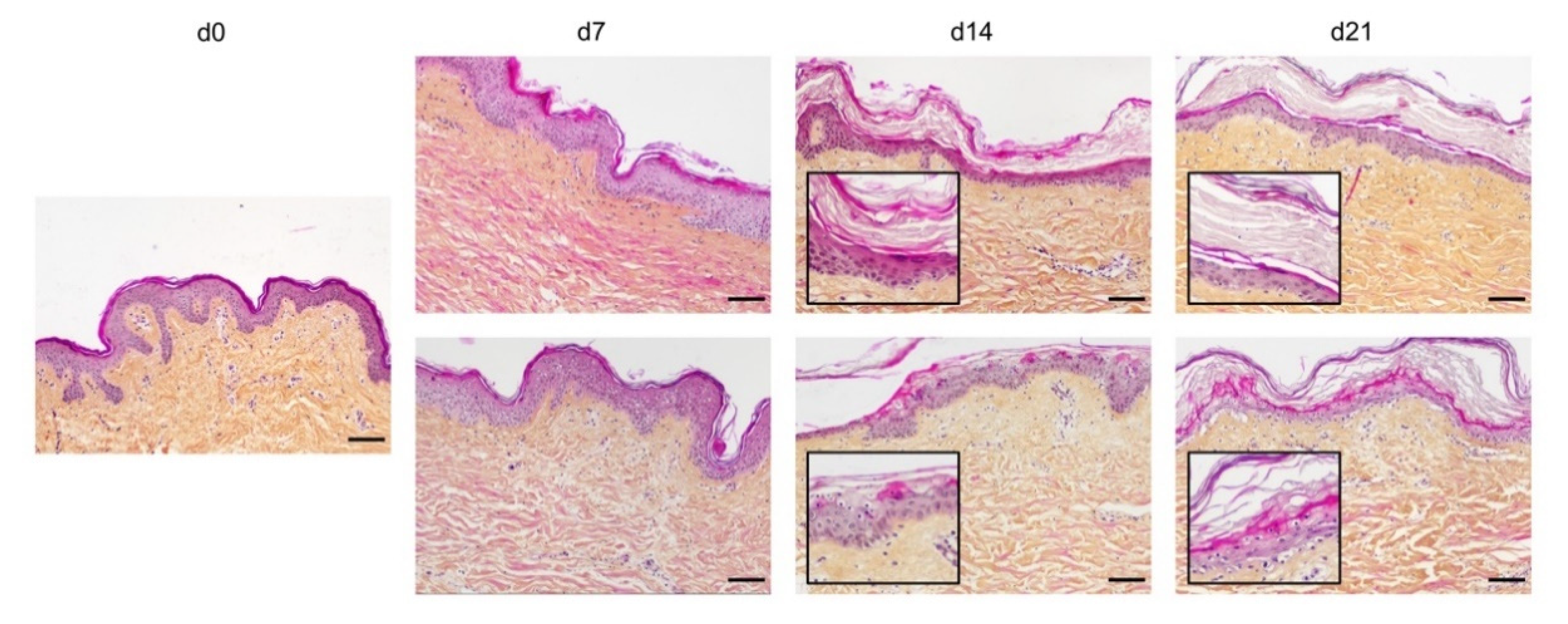
The skin is the largest organ of the body, which meets the environment most directly. Thus, the skin is vulnerable to various damages, particularly burn injury. Skin wound healing is a serious interaction between cell types, cytokines, mediators, the neurovascular system, and matrix remodeling. Tissue regeneration technology remarkably enhances skin repair via re-epidermalization, epidermal-stromal cell interactions, angiogenesis, and inhabitation of hypertrophic scars and keloids. The success rates of skin healing for burn injuries have significantly increased with the use of various skin substitutes. In this review, we discuss skin replacement with cells, growth factors, scaffolds, or cell-seeded scaffolds for skin tissue reconstruction and also compare the high efficacy and cost-effectiveness of each therapy. We describe the essentials, achievements, and challenges of cell-based therapy in reducing scar formation and improving burn injury treatment.

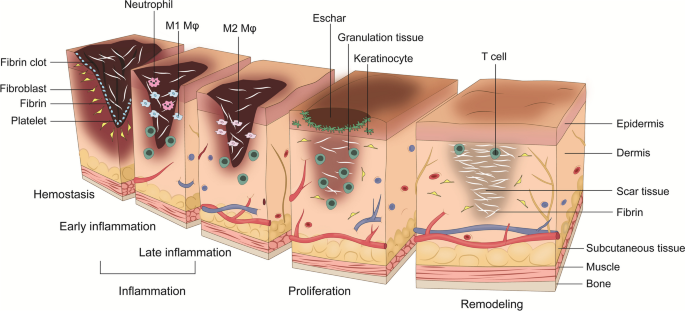
The healing mechanisms of burn wounds. TGF-α transforming growth

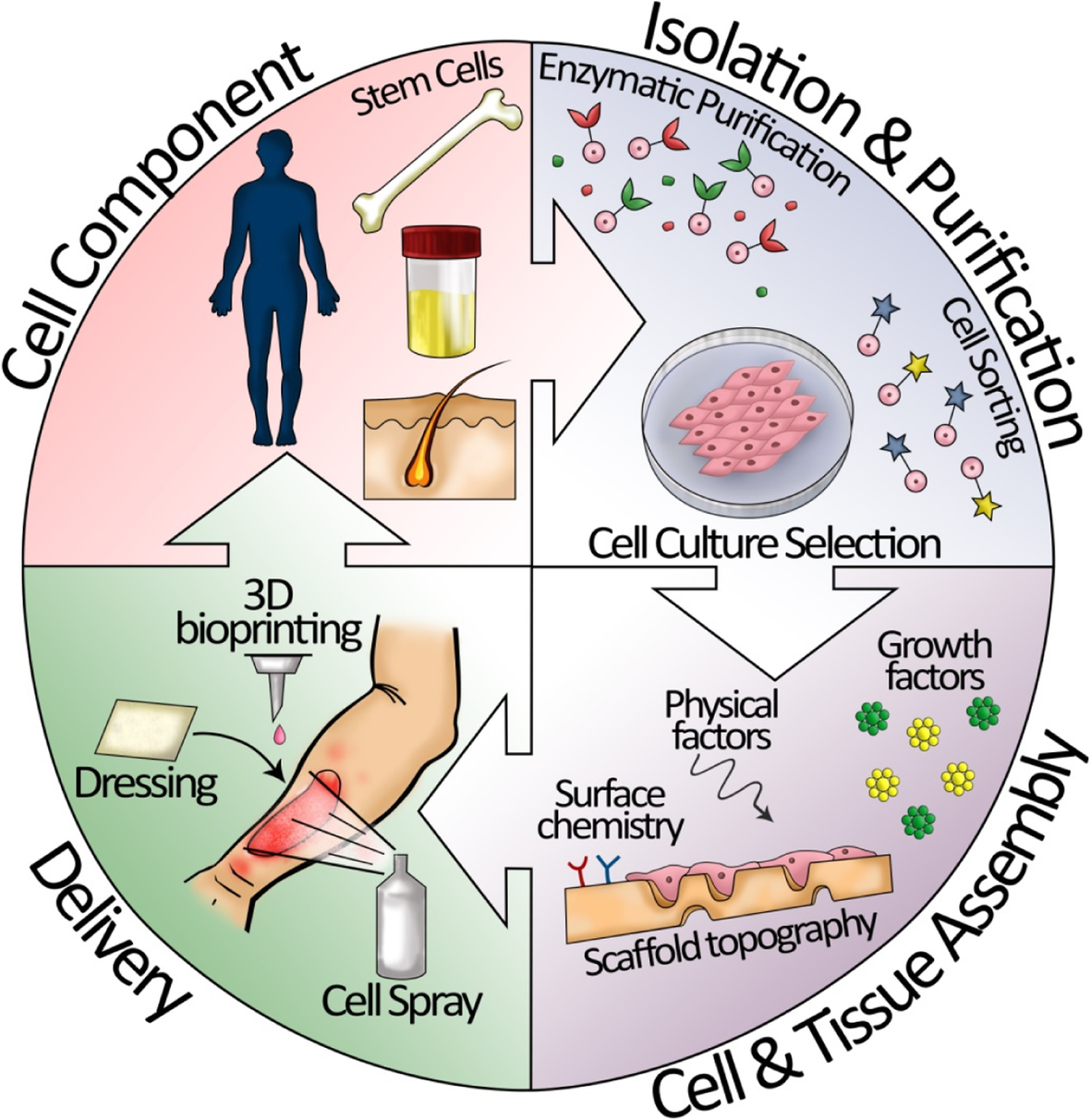
An update on stem cells applications in burn wound healing

Burn Wound Care Musculoskeletal Key
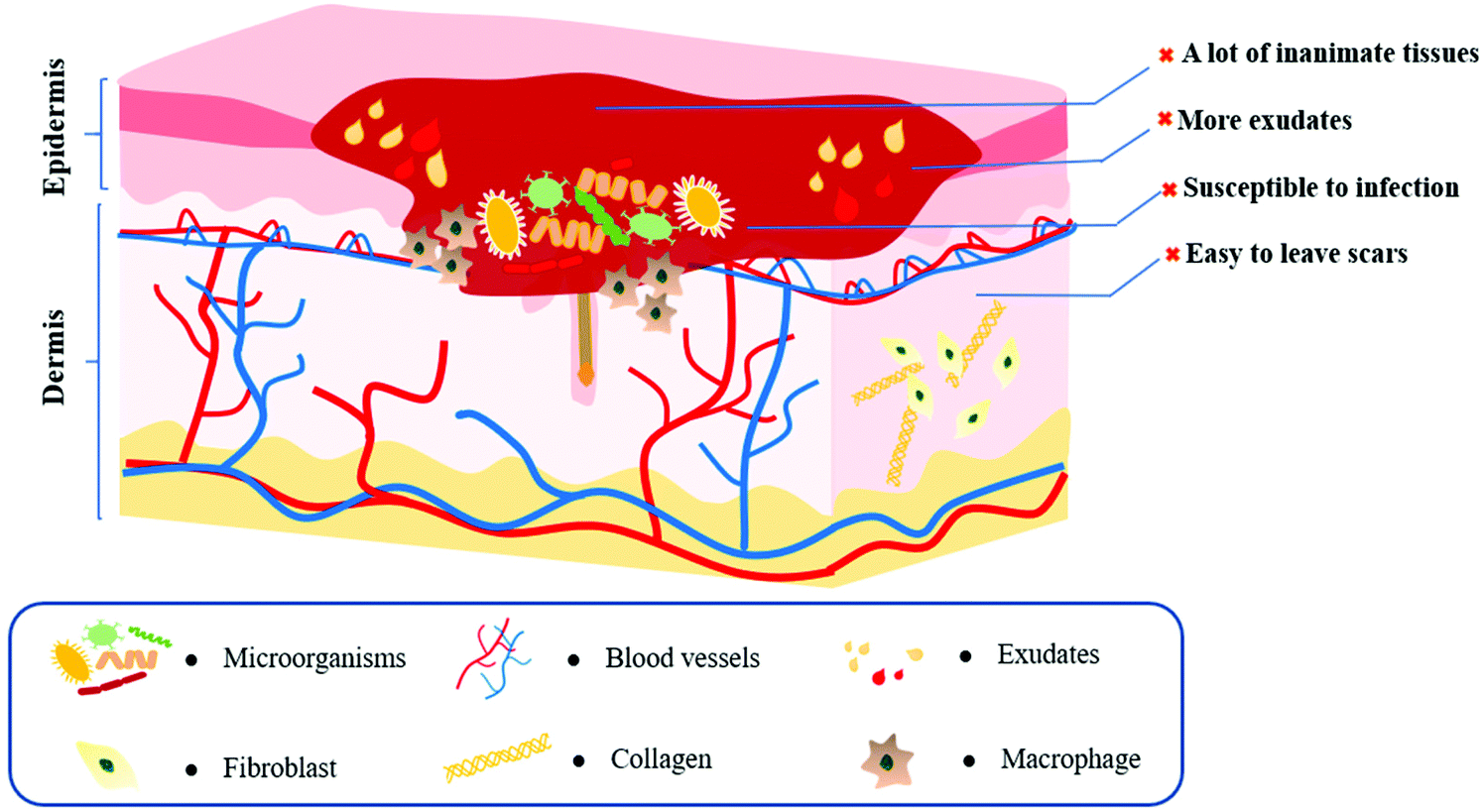
Recent trends on burn wound care: hydrogel dressings and scaffolds
The effect of Ganoderma lucidum spore oil in early skin wound healing: interactions of skin microbiota and inflammation
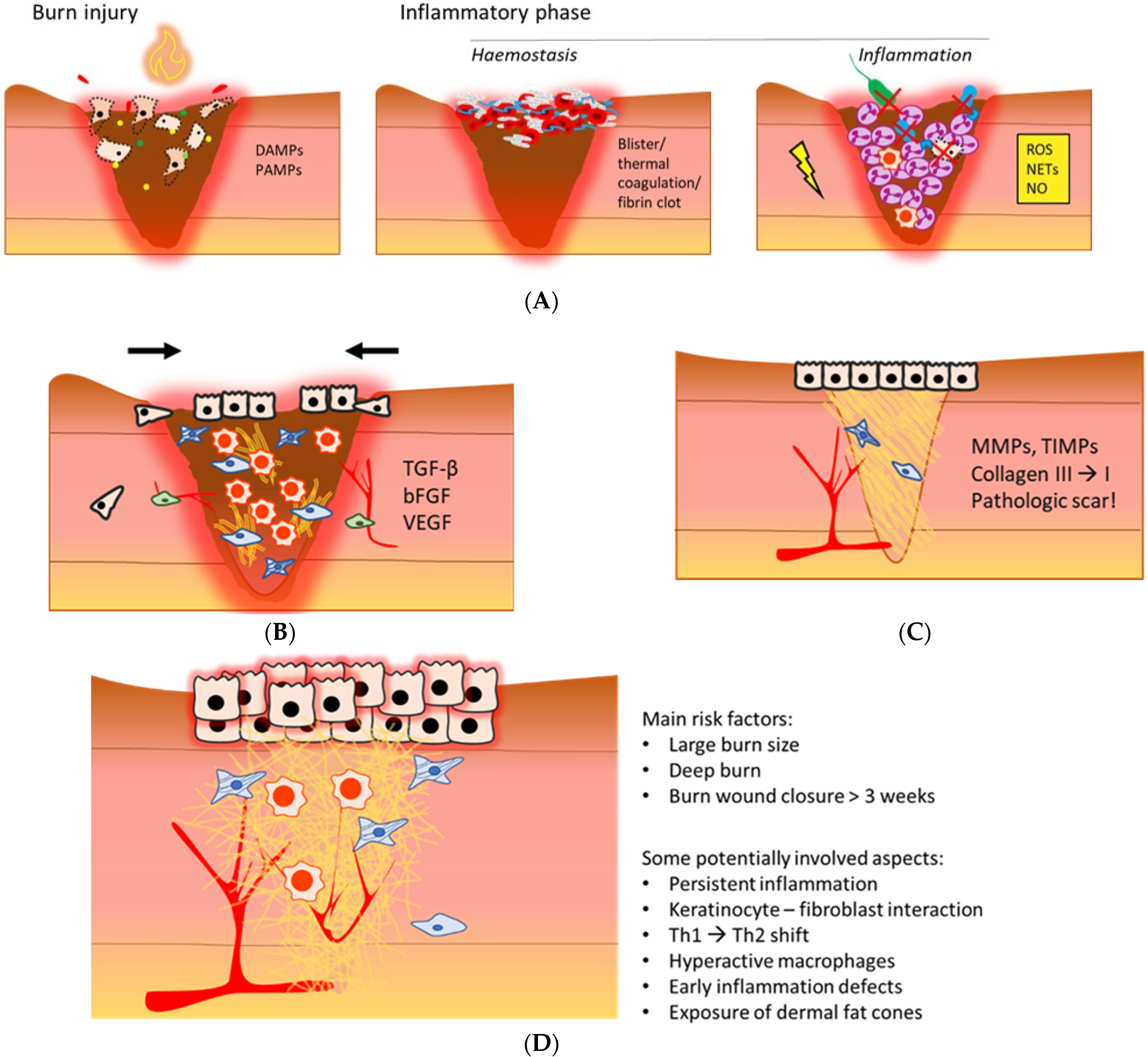
Cells, Free Full-Text
Skin regeneration, repair, and reconstruction: present and future
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Proinflammatory cytokines regulate epidermal stem cells in wound epithelialization, Stem Cell Research & Therapy

The Effects of Argan Oil in Second-degree Burn Wound Healing in Rats
Regulatory T cells in skin regeneration and wound healing

Sufficient therapeutic effect of cryopreserved frozen adipose

Introduction
An active ingredient isolated from Ganoderma lucidum promotes burn wound healing via TRPV1/SMAD signaling
- Introductory Chapter: Concepts of Tissue Regeneration

- The Basics About Stem Cell Treatments & Stem Cell Facts
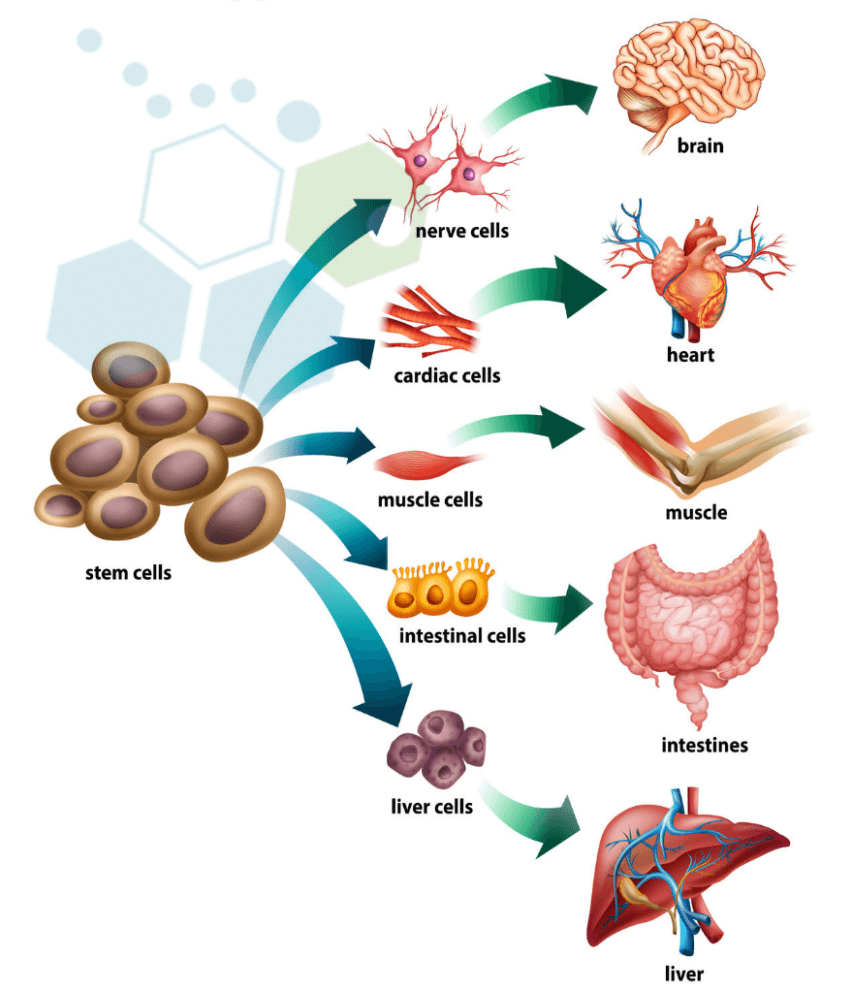
- Figure 1, The steps of regenerative medicine. - StemBook - NCBI Bookshelf

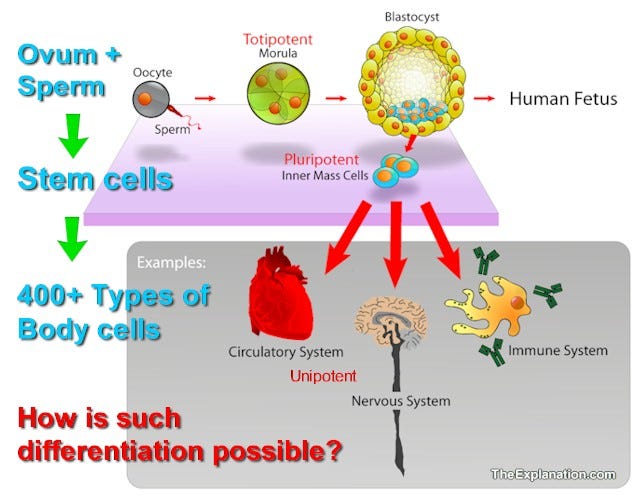
- Stem Cells and Differentiation: the Core of your Body's 24/7/365 Regeneration Process, by Sam Kneller, The Explanation
- Mesenchymal stem cells: immunobiology and role in immunomodulation

- Empyre Loose Fit SK8 Corduroy Light Blue Skate Pants

- What's New – tagged red – Senita Athletics

- Flex Menstrual Discs, Disposable Period Discs, India

- Zone3 Men RX3 Medical Grade Compression Tights Black/Neon Orange Size S-XL

- 25392 – 4-Burner Propane Grill in Stainless w/ LED Controls & Side Burner – Monument Grills