Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery - The Lancet

By A Mystery Man Writer
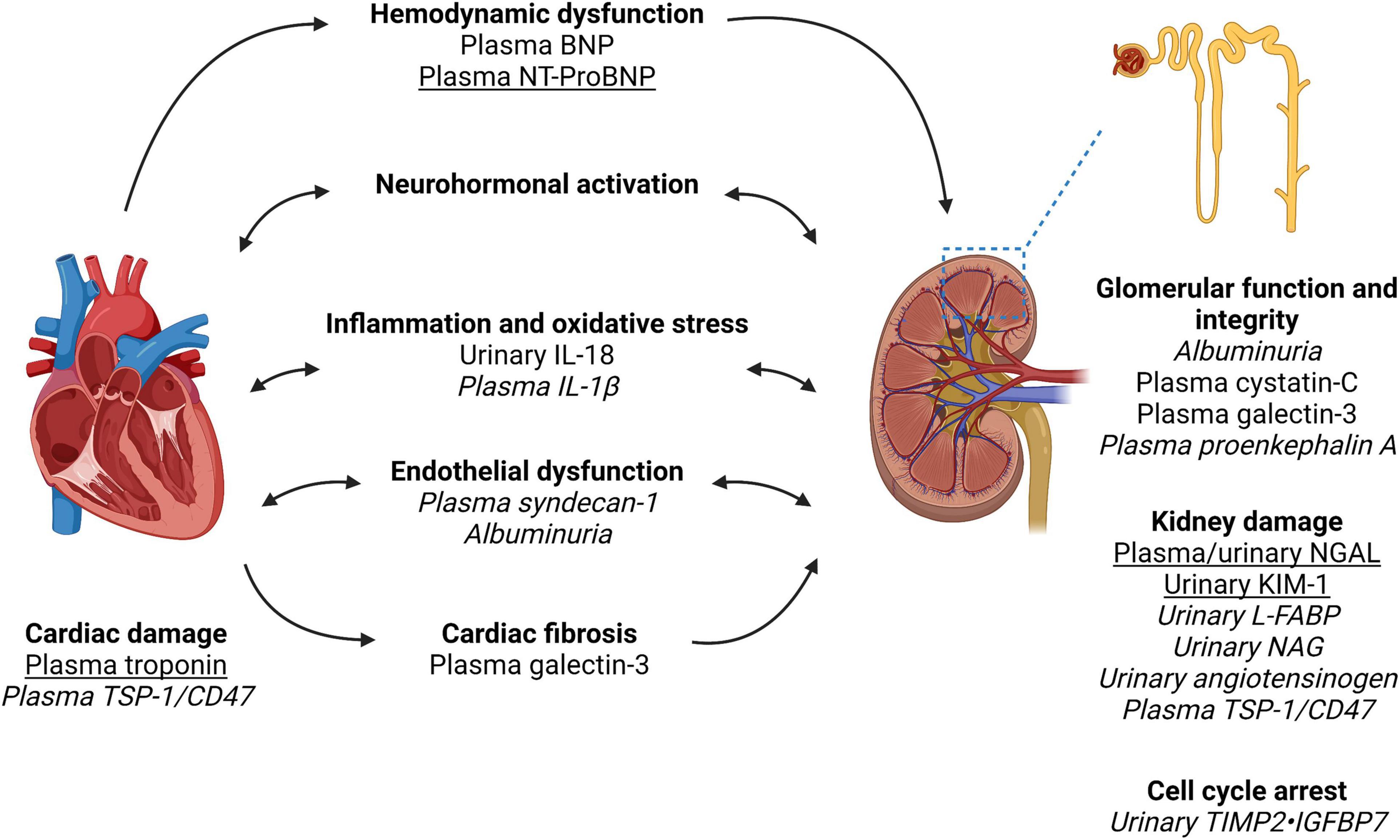
Frontiers Biomarkers in Cardiorenal Syndrome and Potential Insights Into Novel Therapeutics

Plasma and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the diagnosis of new onset acute kidney injury in critically ill patients, Critical Care

Hemojuvelin Predicts Acute Kidney Injury and Poor Outcomes Following Cardiac Surgery
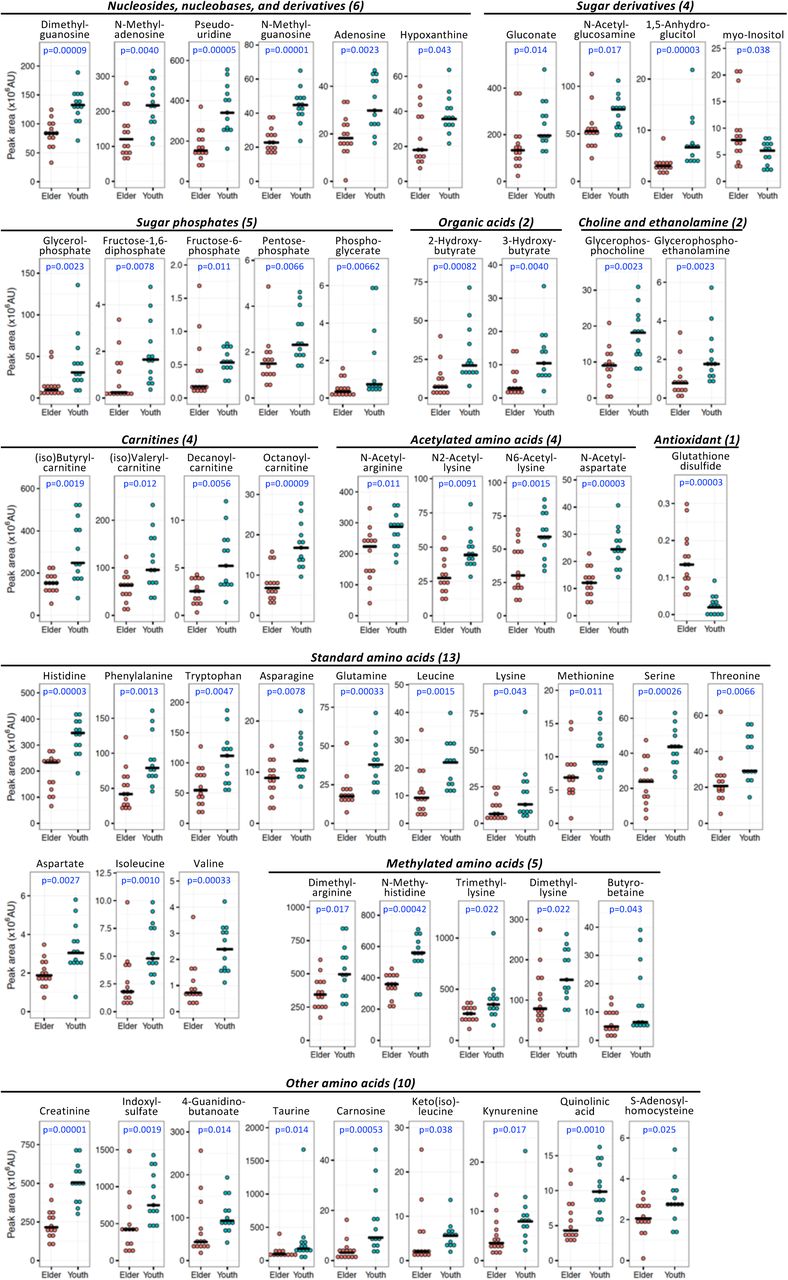
Aging markers in human urine: A comprehensive, non-targeted LC-MS study
Full article: Will urinary biomarkers provide a breakthrough in diagnosing cardiac surgery-associated AKI? – A systematic review

Midkine: A Novel and Early Biomarker of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Interventions
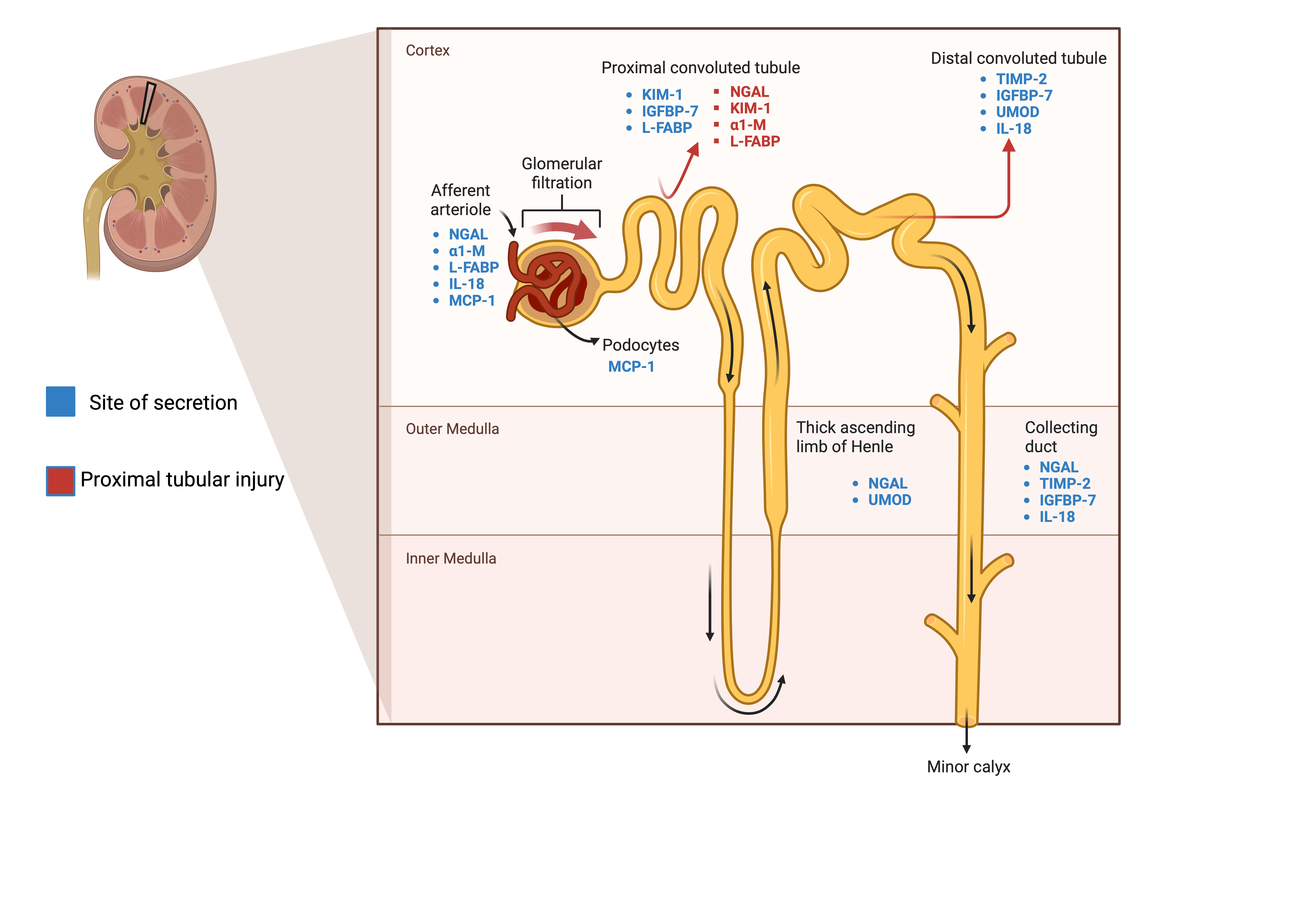
Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury

Overview of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) as a Biomarker in Nephrology

Correlation between Serum Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin and Burn Severity: A Pilot Study

Iron traffics in circulation bound to a siderocalin (Ngal)-catechol complex. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Curve and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Extended-Range Assay: A New Biomarker Approach in the Early Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury and Cardio-Renal Syndrome - ScienceDirect

Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a promising biomarker for human acute kidney injury.

Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts the efficacy of tolvaptan for ascites in patients with liver cirrhosis
- Buy N-Gal Relaxed Fit Nylon Elastane Babydoll with Thong - Black at Rs.500 online

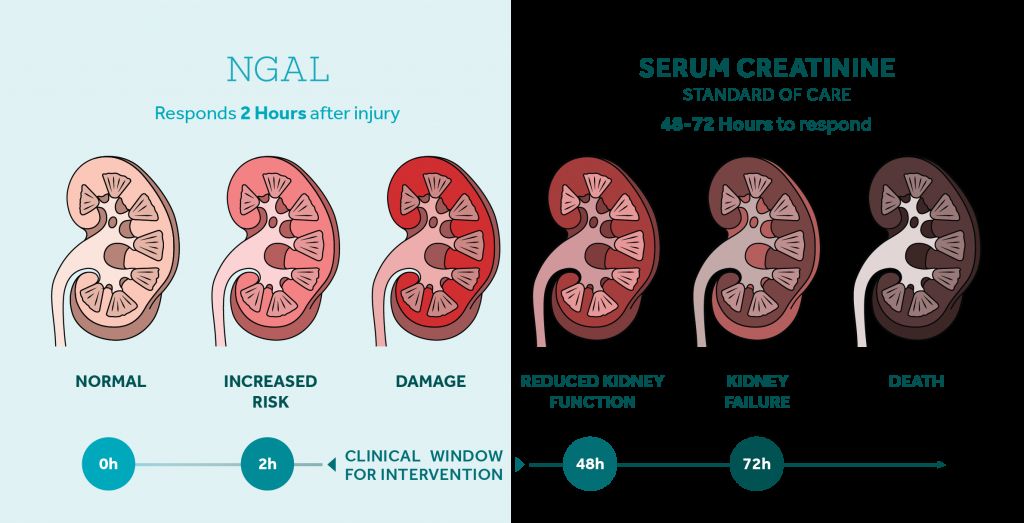
- The Rise and Fall of NGAL in Acute Kidney Injury

- N Gal Pink Lace Women Lingerie Set Td Ls 12 8467195 Htm - Buy N Gal Pink Lace Women Lingerie Set Td Ls 12 8467195 Htm online in India

- Product Recommendations NGAL- Early Marker of Acute Kidney Injury
- N-Gal Gold-Toned Solid Non-Wired Lightly Padded Stick-On Bra

- Womens Sweatshirt 2023 Fall Half … curated on LTK
- SQUATPROOF SENSES+ - Leggings - Trousers - black - Zalando.de

- Huge Multi Sports Collage Soccer Basketball Football Hockey

- Buy Poomex Trendy Bra for Girls and Women's - (Pack of 4) (75cm/30B) Multicolour at

- Is the boreal forest on the edge of a climate change tipping point? - Unearthed
