Figure 5 from Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes

By A Mystery Man Writer
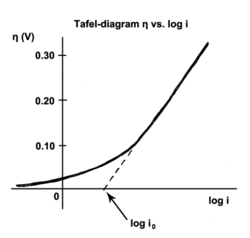
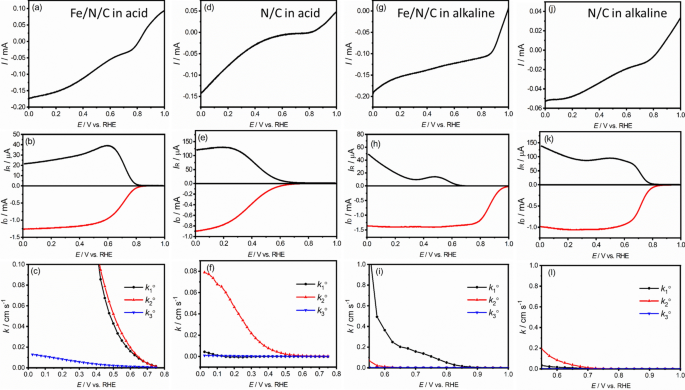
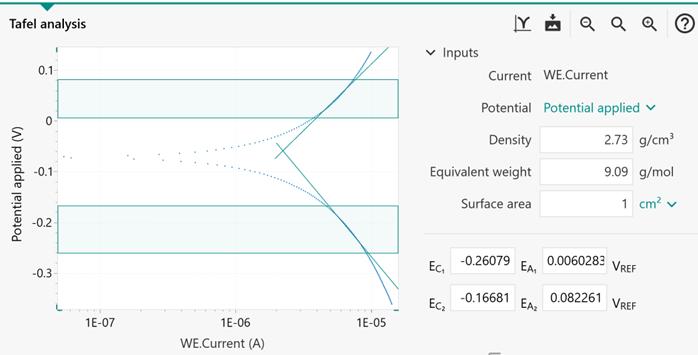
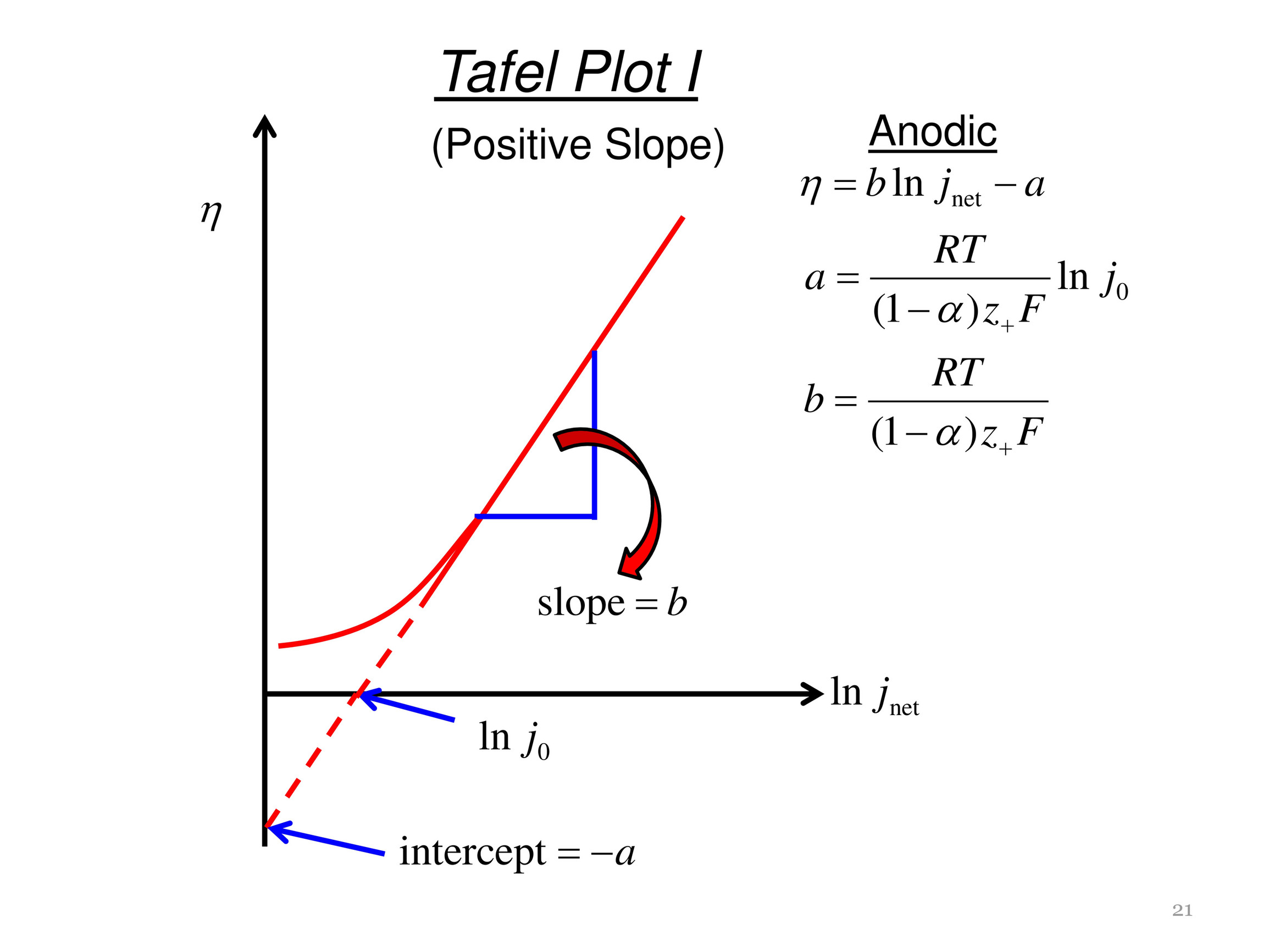
FIGURE 5 | Electrochemical properties of CoP-350, Ru-CoP-1-350, Ru-CoP-2-350 and Pt/C for the HER in 1M KOH. (A,B) HER polarization curves, (C) Tafel plots, (D) Nyquist plots. All measurements were carried out with a fixed catalyst loading of ∼0.3mg cm−−2 on a GCE. - "Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes Derived From a Prussian Blue Analog for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution"

Figure 6 from Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes Derived From a Prussian Blue Analog for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution

Catalysts, Free Full-Text

Figure 2 from Ruthenium Incorporated Cobalt Phosphide Nanocubes Derived From a Prussian Blue Analog for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution

Recent advances in cobalt phosphide-based materials for electrocatalytic water splitting: From catalytic mechanism and synthesis method to optimization design - ScienceDirect

Hollow Cobalt Phosphide with N-Doped Carbon Skeleton as Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Overall Water Splitting

Hybrid materials: state of the art and new frontiers

Efficient Nitrate-to-Ammonia Electroreduction at Cobalt Phosphide Nanoshuttles
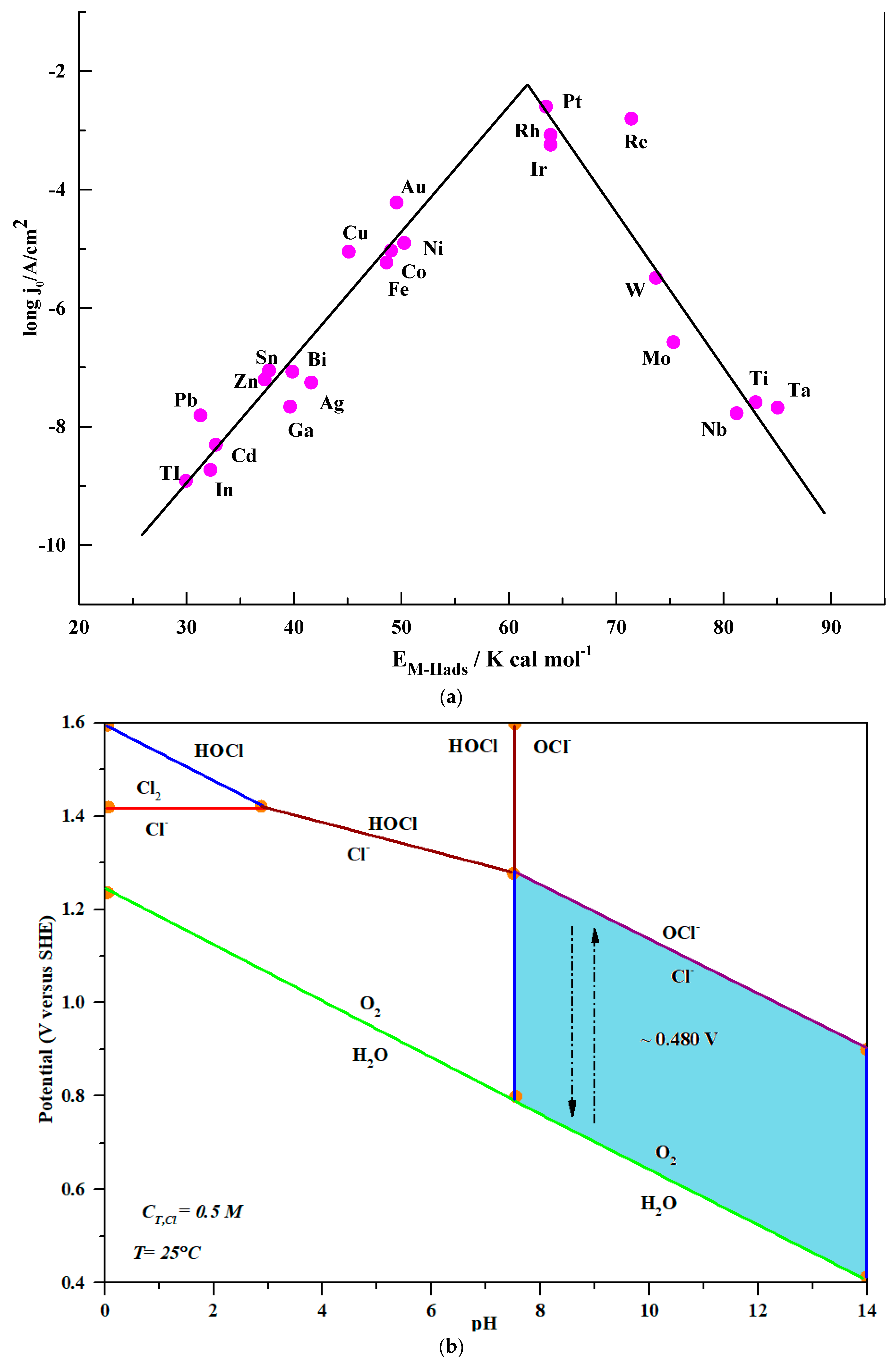
Sustainability, Free Full-Text

Crystals, Free Full-Text
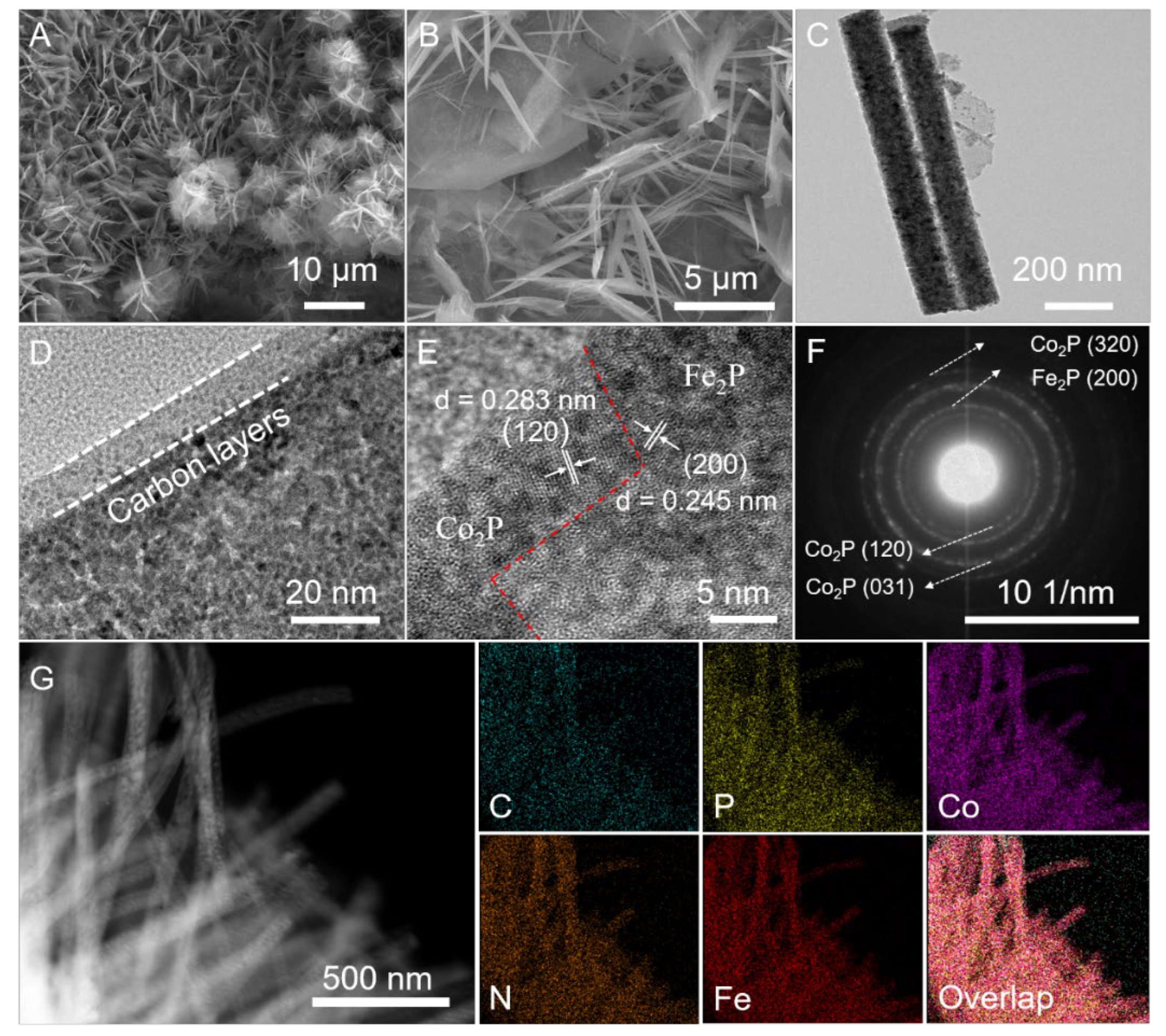
Catalysts, Free Full-Text

PDF) Enhanced ethanol oxidation over Pd nanoparticles supported porous graphene-doped MXene using polystyrene particles as sacrificial templates

Ruthenium-cobalt nanoalloys encapsulated in nitrogen-doped graphene as active electrocatalysts for producing hydrogen in alkaline media

Recent advances in earth-abundant first-row transition metal (Fe, Co and Ni)-based electrocatalysts
UofT Solar Fuels Cluster

SEM images of (A,B) Co-PBA, (C) Ru-Co-PBA-2 and (D) Ru-CoP-2-350.
- Core Home Fitness Adjustable Dumbbell Set review

- American Chino Short - Khaki, Gustin Chinos

- WXNLB Mens Minimizer Corset Back Support Shockproof Sports Fitness Vest Chest Binder Trans Tank Top Bustiers Underwear (Color : Black, Size : X-Large)

- Chanting Mala Prayer Beads 108 Necklace Bracelet for Meditation with Tiny Lotus Flower Charm

- NWT TORRID CURVE WIRE FREE LIGHTLY LINED EVERYDAY BRA, SIZE 36H